Ebook Harrison''s manual of medicine (16th edition): Part 2
➤ Gửi thông báo lỗi ⚠️ Báo cáo tài liệu vi phạm

Nội dung chi tiết: Ebook Harrison''s manual of medicine (16th edition): Part 2
Ebook Harrison''s manual of medicine (16th edition): Part 2
SECTION 8CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES117PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE HEARTGeneral examination of a pt with suspected heart disease should include vital sign Ebook Harrison''s manual of medicine (16th edition): Part 2ns (respiratory rate, pulse, blood pressure), skin color, clubbing, edema, evidence of decreased perfusion (cool and sweaty skin), and hypertensive changes in optic fundi. Important findings on cardiovascular examination include:CAROTID ARTERY PULSE (Fig. 117-1)•Pulsus parvus: Weak upstroke due to d Ebook Harrison''s manual of medicine (16th edition): Part 2ecreased stroke volume (hypovolemia. LV failure, aortic or mitral stenosis).•Pulsus tardus: Delayed upstroke (aortic stenosis).•Bounding (hyperkineticEbook Harrison''s manual of medicine (16th edition): Part 2
) pulse: Hyperkinetic circulation, aortic regurgitation. patent ductus arteriosus, marked vasodilatation.•Pulsus hisferiens: Double systolic pulsationSECTION 8CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES117PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE HEARTGeneral examination of a pt with suspected heart disease should include vital sign Ebook Harrison''s manual of medicine (16th edition): Part 2s paradoxus: Exaggerated inspirator}' fall (>10 mmHg) in systolic bp (pericardial tamponade, severe obstructive lung disease).JUGULAR VENOUS PULSATION (JVP) Jugular venous distention develops in right-sided heart failure, constrictive pericarditis, pericardial tamponade, obstruction of superior vena Ebook Harrison''s manual of medicine (16th edition): Part 2 cava. JVP normally falls with inspiration but may rise (Kussmaul’s sign) in constrictive pericarditis. Abnormalities in examination include:•Large “aEbook Harrison''s manual of medicine (16th edition): Part 2
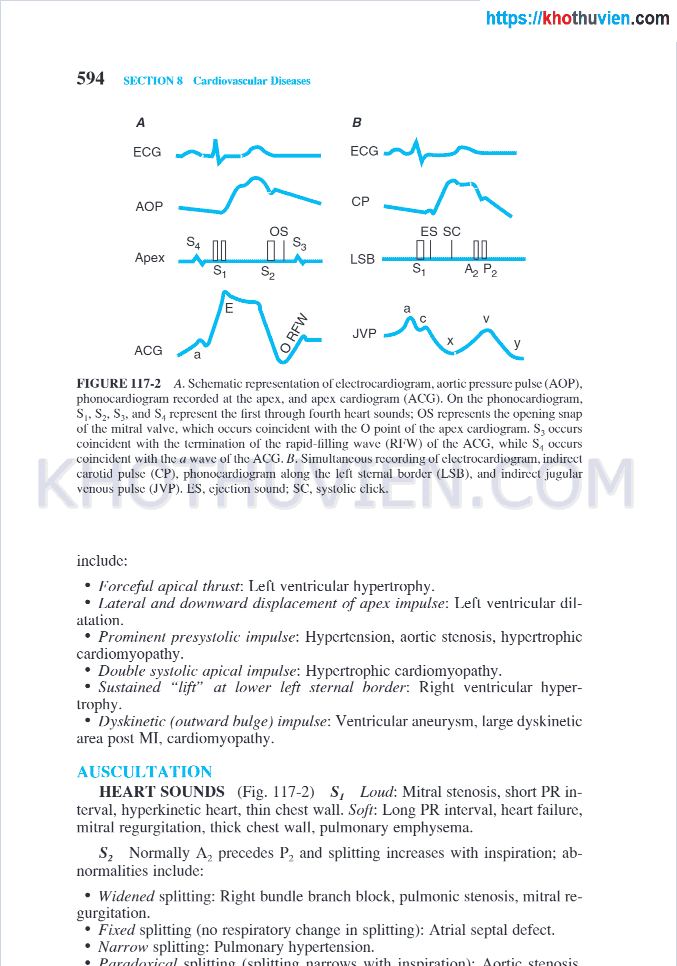
" wave: Tricuspid stenosis (TS), pulmonic stenosis, AV dissociation (right atrium contracts against closed tricuspid valve).•Large “v” wave: TricuspidSECTION 8CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES117PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE HEARTGeneral examination of a pt with suspected heart disease should include vital sign Ebook Harrison''s manual of medicine (16th edition): Part 2apical impulse is normally localized in the fifth intercostal space, midclavicular line (Pig. 117-2). AbnormalitiesA. Hypokinetic Pulse B. Parvus et Tardus Pulse c. Hyperkinetic PulseD. Bisferiens PulseE. Dicrotic Pulse + Alternans594 SECTION 8 Cardiovascular DiseasesAFIGURE 117-2 A. Schematic repre Ebook Harrison''s manual of medicine (16th edition): Part 2sentation of electrocardiogram, aortic pressure pulse (AGP), phonocardiogram recorded al the apex, and apex cardiogram (ACG). On the phonocardiogram.Ebook Harrison''s manual of medicine (16th edition): Part 2
S|. S2. Sj. and s., represent the lirsl through fourth heart sounds; OS represents the opening snap of (he mitral valve, which occurs coincident with SECTION 8CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES117PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE HEARTGeneral examination of a pt with suspected heart disease should include vital sign Ebook Harrison''s manual of medicine (16th edition): Part 2ith the a wave of the ACG. IÌ. Simultaneous recording of electrocardiogram, indirect carotid pulse (CP), phonocardiogram along the left sternal border (LSB). and indirect jugular venous pulse (JVP). 1ĨS. ejection sound; sc. systolic click.include:•borceful apical thrust: Left ventricular hypertrophy Ebook Harrison''s manual of medicine (16th edition): Part 2.•Lateral and downward displacement of apex impulse: Left ventricular dilatation.•Prominent presystolic impulse: Hypertension, aortic stenosis, hypertEbook Harrison''s manual of medicine (16th edition): Part 2
rophic cardiomyopathy.•Double systolic apical impulse: Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.•Sustained "lift" at lower left sternal border: Right ventricular hSECTION 8CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES117PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE HEARTGeneral examination of a pt with suspected heart disease should include vital sign Ebook Harrison''s manual of medicine (16th edition): Part 2-2) s, Loud: Mitral stenosis, short PR interval. hyperkinetic heart, thin chest wall. Soft: Long PR interval, heart failure, mitral regurgitation, thick chest wall, pulmonary emphysema.s2 Normally A? precedes P2 and splitting increases with inspiration: abnormalities include:•Widened splitting: Righ Ebook Harrison''s manual of medicine (16th edition): Part 2t bundle branch block, pulmonic stenosis, mitral regurgitation.•Fixed splitting (no respiratory change in splitting): Atrial septal defect.•Narrow splEbook Harrison''s manual of medicine (16th edition): Part 2
itting: Pulmonary hypertension.SECTION 8CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES117PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE HEARTGeneral examination of a pt with suspected heart disease should include vital signSECTION 8CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES117PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE HEARTGeneral examination of a pt with suspected heart disease should include vital signGọi ngay
Chat zalo
Facebook
